Week 12
- Daniel
- Jul 13, 2021
- 2 min read
Hi again, it's me, the legendary . I hope all of you guys had a wonderful holiday. During this week, we were introduced to digital fabrication, which is an important topic as our society is becoming more digitalised. In fact, in Germany, the first world 3d printed house has been built, as seen in the illustration below.

Figure 1: (Ozdemir et al., 2021)
Digital fabrication has many advantages, such as:
Additive technology in the Oil & gas industry
Low cost for high complexity materials
Shorten supply chain
Generative & iterative design
Good for prototyping
Physical evaluation of product
Testing can be done on product
Help in identifying errors
Good for end use parts
Increase the lifespan of older equipment by recreating them
Recreating high value/ low volume End-Use products
Afterwards, we had to do a presentation to the class explaining “What is additive manufacturing (AM)?” as well as, the different types of 3D printing technologies, Fusion Deposition Modelling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
So what is AM? It makes use of a computer 3D modelling software (Computer Aided Design CAD) machine equipment. With the help of a sketch, it uses a layer-upon-layer technology to create a 3D product.
FDM- Creates a 3D product by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament using the printer nozzle, and deposits the melted filament layer by layer, as seen in figure 2.

Figure 2: Schematic of FDM process(Alafaghani, 2021)
SLA - This model utilises uv-laser technology to cure photopolymer resin into hardened plastic. The resin is either poured by the user, or dispensed automatically by the machine. The build platform is then slowly lowered into the resin, leaving only a thin layer of resin between the platform and the bottom of the tank. The laser is shone through the platform, hardening the resin in the layer of resin. The platform then rises and repeats the process layer by layer to print out the object.

Figure 3: Schematic of SLA process (Negi, 2021)
SLS- It uses a high power laser to fuse small particles of polymer powder. The machine first levels the polymer powder by having a roller spread it into a thin layer. It then uses the laser to heat and fuse the material together. This process is then repeated for the remaining layers. Seen figure 3.
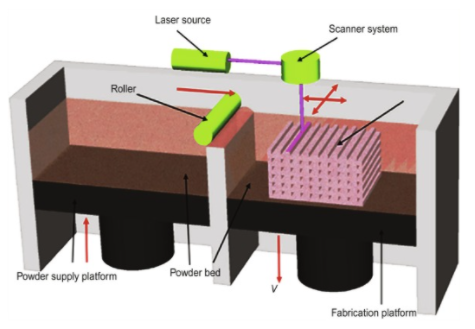
Figure 4: Schematic of SLS process (Manuel Garcia-Leiner, 2021)
After our presentation, we got to listen to the other group's presentations. For example, we learned that with the help of FDM, we are able to create vegetarian meat. We also learned how to choose a suitable thermoplastic for FDM printing, as well as how to create a quality printout and increase the speed of printing, along with the factors affecting the quality and printing speed such as layer height, print speed. We also learned about how defects such as overhang and bridging will appear in a FDM 3D printing.
Done by
Daniel
Comments